Meet Reynard the Robot
Introduction
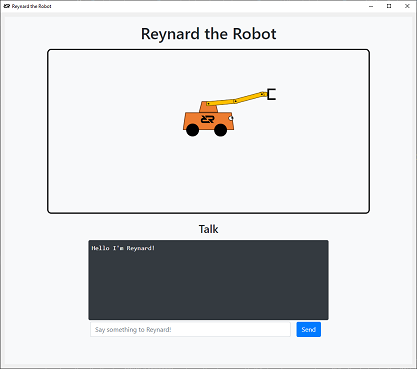
Reynard the Robot is a simple cartoon robot designed to help users learn the Robot Raconteur communication framework, and also learn how to develop interfaces for various devices and software components. Reynard is implemented as a simple Python package that uses a web browser to display the robot and its user interface. The base of the robot can be translated in the X and Y directions, and robot arm has three revolute joints, for a total of 5 degrees of freedom. The user interface also provides a simple chat window to send and receive messages.
Installation
Reynard the Robot is a simple Python package that can be installed using pip. To install Reynard the Robot, use the following command:
python -m pip install reynard_the_robot
On Linux, it may be necessary to use python3 instead of python. Use python3 in all future
commands if this is the case. It may also be necessary to install the python3-pip package on Linux. On Ubuntu and
Debian, run sudo apt-get install python3-pip to install pip for Python 3.
Start Reynard the Robot Server
Most of the examples in the Robot Raconteur documentation use Reynard the Robot as an example. To start Reynard the Robot as a Robot Raconteur service, use the following command:
python -m reynard_the_robot
Remember to use python3 instead of python on Linux if necessary.
With the server running, open a web browser to the address http://localhost:29201 to see Reynard the Robot!
The Robot Raconteur server is now and can be connected to using the Robot Raconteur client libraries. The following is an example of a Python client that connects to the Reynard the Robot server:
from RobotRaconteur.Client import *
c = RRN.ConnectService('rr+tcp://localhost:29200?service=reynard')
c.say("Hello from Robot Raconteur client!")
Reynard the Robot as a Python Package
Run the following script to run Reynard the Robot directly from Python as a Python class:
from reynard_the_robot import Reynard
reynard = Reynard()
reynard.start()
reynard.say("Hello, I am Reynard the Robot!")
reynard.teleport(100,200)
input("Press enter to exit")
Run the script using Python, and open a web browser to the address http://localhost:29201 to see Reynard the Robot.
Remember to use python3 instead of python on Linux if necessary.
Reynard the Robot Control Interfaces
Robots, industrial devices, and software components have a myriad of possible software interfaces. These interfaces can be simple digital/analog signals, serial communication, network communication, proprietary protocols, software application programming interfaces (APIs), and more. These various software interfaces can be bewildering to programmers and system integrators who are trying to make these devices work together. Reynard the Robot is designed to be representative of the types of interfaces that are commonly found in real-world devices and software components. Reynard the Robot implements several of these interfaces to help users learn how to develop interfaces for various devices and software components.
The following interfaces are provides:
Python Library API
Robot Raconteur Service
HTTP REST API
Raw ASCII Socket
ROS 1 (external package required)
ROS 2 (external package required)
See the Reynard the Robot Documentation for details on how to use these various interfaces.
The Robot Raconteur documentation uses Reynard the Robot as an example to demonstrate how to use the Robot Raconteur communication framework. The documentation will also show how to use the various interfaces to develop Robot Raconteur drivers.